Although compounding may occur in different settings, it is most commonly
done in pharmacies. Compounding in general is a practice where a licensed
pharmacist, a licensed physician, or in the case of an outsourcing facility,
a person under the direct supervision of a licensed pharmacist, combines,
mixes, or alters the ingredients of a drug to create a sterile or non-sterile
preparation tailored to the needs of individual patients.
These are usually provided when an FDA-approved drug is not medically
suitable for the treatment of a patient. Example of which can be when someone
is allergic to a certain dye and needs a medication to be made without it.
Another scenario would be of an elderly patient or a child who is unable to
swallow a tablet or capsule, hence requiring a medicine in a liquid dosage
form.
Compounded drugs serve an important medical need for patients, but at the
same time may present certain risks as they do not have the same safety,
quality, and efficacy validation as compared to approved drugs.
Drugs compounded in outsourcing facilities are subject to current good
manufacturing practice (CGMP) requirements. While, drugs compounded by a
licensed pharmacist in a state-licensed pharmacy, or federal facility, or by
a physician, in accordance with the conditions of section 503A of the Federal
Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act), are exempt from compliance with CGMP
requirements; however, these facilities can still be subject to less
stringent quality standards set per state.
Regardless of where compounding occurs (e.g., pharmacy, outsourcing facility,
physician’s office), these drugs must not be prepared, packed, or held under
insanitary conditions. Poor compounding practices can cause serious drug
quality problems, such as contamination or dispensing of medications that do
not possess the strength, quality, and purity that the drugs are supposed to
have; these factors can then lead to serious patient injury and death.
Esco Healthcare provides specialist services, equipment packages, and process
solutions from our core platform products. Together with its wide range of
innovative and turnkey solutions, backed with its four (4) core technologies,
Esco Healthcare enables various industries such as pharmaceuticals,
nutraceuticals, and cosmeceuticals to comply with the internationally
accredited GMP, as well as, industrial, environmental, and health and safety
standards.
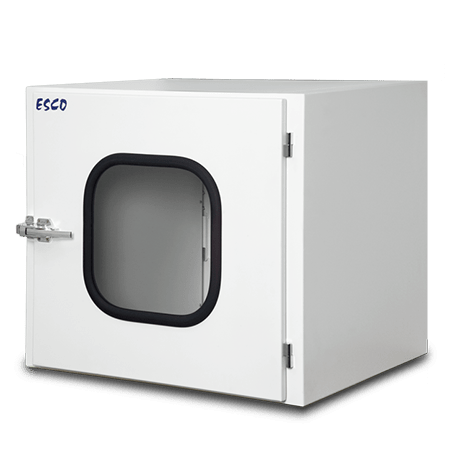
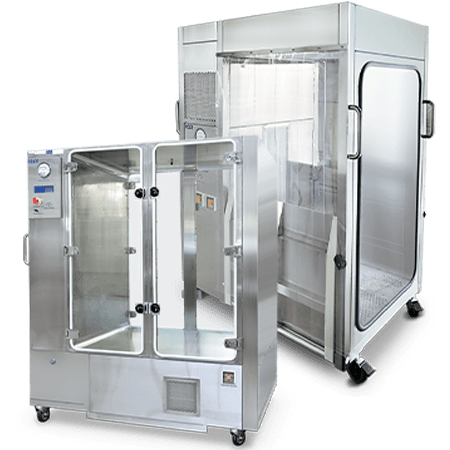
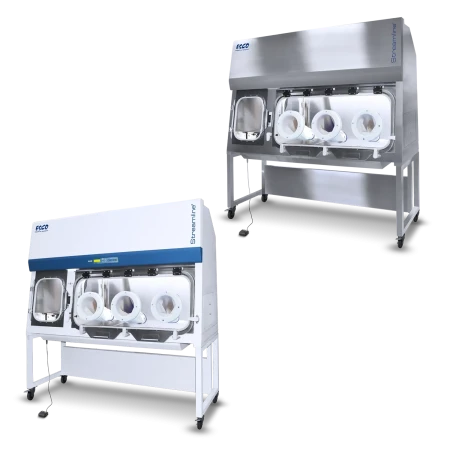
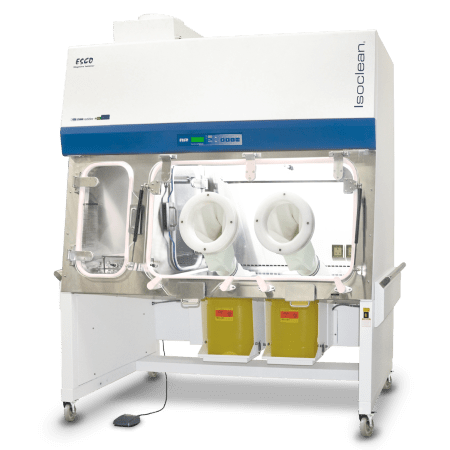
Compounding Aseptic Isolator (CAI)
Designed in accordance with the United States Pharmacopeia General Chapter <797> guidelines, Esco Healthcare’s CAI ensures a sterile/aseptic compounding environment within the isolator at all times, from compounding up to material transfer operations.
Understanding CAI
Esco Healthcare’s Compounding Aseptic Isolator (CAI) provides a safe and
clean environment for compounding of
non-hazardous, sterile drug preparations and IV admixtures in
compliance with USP <797> criteria.
The work zone and pass-through interchange are under positive
pressure to the room to maintain sterility in case of breach in the barrier
isolation system. Air cleanliness is maintained with the use HEPA filters and
other filters capable of eliminating microbial and other particulate
contaminants
Key Applications:
-
Aseptic Compounding
-
Total Parenteral Nutrition Formulation
-
Sterile Filling Line
-
Cell Therapy
-
Gene Therapy
-
Tissue Engineering
-
Batch Sterility Testing
-
Cosmetic / Cosmeceuticals
Advantages of Esco Healthcare’s CAI
One of the requirements of USP <797> is to ensure that air from the ambient environment going into the isolator must first pass through microbially retentive filters (HEPA at minimum). As such, Esco Healthcare’s Compounding Aseptic Isolators (CAI) are designed with a standard HEPA (H14) filtration system with a 99.995% filtration efficiency at 0.1 to 0.3 microns, thus, providing an ISO Class 5 air quality in the chambers (as per ISO 14644-1).
Pressure Regime
For CAI and sterile compounding, the system operates under a standard positive pressure of + ≥37 Pa in the work zone and + ≥25 Pa in the pass-through chamber. This design guarantees the removal of cross-contamination risk from the surrounding environment towards the isolator chambers, which in turn ensures the provision of sterile and high-quality final compounded sterile products (CSPs).
Airflow Regime
Recirculating airflow can be applied for compounding non-hazardous sterile drugs. In a recirculating airflow regime, about 90% of HEPA-filtered air is recirculated within the isolator while approximately 10% of air is exhausted through such filters to prevent heat build-up in the system. The exhausted air will then be replenished by ambient air coming from the top in-let G4 pre-filters with 80% efficiency.
Ensuring Sterility
Sterility is key in compounding aseptic/sterile products as any contamination
to the final product may result to a serious adverse event for patients which
may even cause irreparable damage to the image of the institution.
CAI systems help ensure maintenance of sterility as they provide
complete separation between the operators/surrounding environment and the
actual process. As such, unlike open-front cabinets (laminar flow benches and
biological safety cabinets), CAI units are not highly dependent on aseptic
technique of the operator, although proper training and annual retraining of
all operators involved in sterile compounding, must still be observed.
Another way of ensuring sterility in the work zone of the CAI is
to have a proper maintenance service of the isolator system. Guidelines
suggest annual recertification of the unit is important to ensure that it
still provides the same quality of service similar to its integrity during
initial installation. In line with this is the importance of
having a proper cleaning/decontamination process for the isolator system.
Note that the frequency of this will depend on each facility's services.
-
Decontamination Process
involves the proper removal of residues in the work zone through the use of agents such as: sterile alcohol, sterile water, peroxide, or sodium hypochlorite.
-
Cleaning Process
is the step of removing both inorganic and organic materials from the work zone via germicidal detergents and sterile water.
-
Disinfection Process
this is the act of destroying microorganisms that might be present in the work zone through the use of sterile alcohol or other EPA-registered disinfectants.
Each compounding facility has its own protocols for various processes, and understanding the needs of each process is critical in choosing the correct equipment that will help protect the actual sterile compounded product as well as the operator and the environment from untoward exposure or cross-contamination.
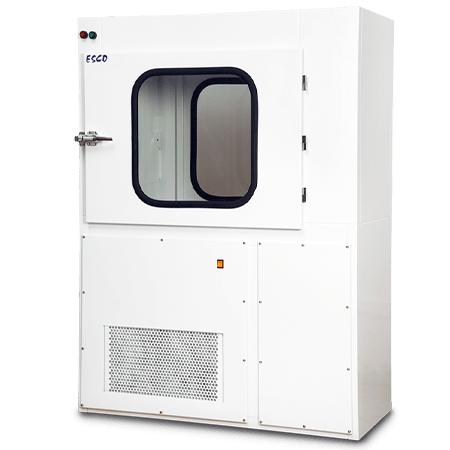
Compounding Aseptic Containment Isolator (CACI)
The Compounding Aseptic Containment Isolator (CACI) by Esco Healthcare is designed in compliance with the United States Pharmacopeia General Chapter <797> and <800> guidelines. It aims to provide a safe and clean environment for compounding of sterile hazardous drug preparations in.
Understanding CACI
Compounding Aseptic Containment Isolator (CACI) provides a safe and clean
environment for compounding of hazardous, sterile drug preparations in
compliance with USP 797 and 800 criteria. It is suitable for work involving
hazardous materials, antineoplastic, or cytotoxic compounding
applications.
The work zone and pass-through chambers are under negative pressure
to maintain operator protection in case of a breach in the barrier isolation
system. Clean air within the work zone must be supplied through a microbial
retentive filter (HEPA minimum) system capable of containing airborne
concentrations of the physical size and state of the drug being
compounded.
During processes involving handling of volatile hazardous drugs,
air must be externally vented from the isolator through a properly designed
and dedicated building exhaust. This is the premium solution for every
pharmacy’s compounding and containment needs.
Key Applications:
-
Potent Formulation
-
Aseptic Formulation
-
Sterile/Aseptic Compounding
-
Chemotherapy Compounding
-
Contained Powder Handling
-
Pharmacy Cytotoxic Compounding Isolator
-
Sub-division Isolator
-
Off-loading Containment Isolator
Advantages of Esco Healthcare’s CACI
Esco Healthcare’s Compounding Aseptic Containment Isolators (CACI) are designed with a standard HEPA (H14) filtration system with a 99.995% filtration efficiency at 0.1 to 0.3 microns, thus, providing an ISO Class 5 air quality in the chambers (as per ISO 14644-1). Options for a HEPA bag-in, bag-out (BIBO) exhaust filtration system is available for safe filtration change.
Pressure Regime
Negatively pressured and ISO 10648-2 Class 3 pressure leak tight CACI units, operate under a standard regime of -37 Pa in the work zone and -25 Pa in the pass-through chamber. This design ensures containment of the hazardous/toxic materials handled inside the isolator while also maintaining a sterile work zone to uphold the integrity and high quality of compounded sterile products (CSPs).
Airflow Regime
Esco Healthcare’s CACI units can be configured to have a recirculating or
total exhaust/single pass airflow system. In a recirculating airflow regime,
about 90% of HEPA-filtered air is recirculated within the isolator while
approximately 10% of air is exhausted through such filters to prevent heat
build-up in the system. The exhausted air will then be replenished by ambient
air coming from the top in-let G4 pre-filters with 80% efficiency. This
airflow regime can be recommended for compounding facility’s not handling
volatile hazardous drugs, especially for institutions that do not have the
capacity for a 100% exhaust/ducting system.
However, as per USP <800> guidelines, for facility’s handling
volatile hazardous drugs/substances it is better to have a total
exhaust/single pass equipment that will be connected to a ducting/exhaust
system. It must be understood that HEPA filters are for the removal of
particles (0.1 to 0.3micron sizes) and are not designed for filtration of
gases or volatile materials. As such, the sure way to fully remove the
volatile materials from the isolator and from the facility is to duct the
isolator to a dedicated building exhaust system. The airflow for this total
exhaust/single pass isolator ensures that all air passing through the supply
HEPA filters will also be exhausted out through a series of HEPA exhaust
filter system (option for BIBO).
Each compounding facility has its own protocols for various
processes, and understanding the needs of each process is critical in
choosing the correct equipment that will help protect the actual sterile
compounded product as well as the operator and the environment from untoward
exposure or cross-contamination.
References:
- Morrow, T. & Felcone, L. (2004). Defining the difference: What Makes Biologics Unique. Biotechnology Healthcare, 1(4), 24-26, 28-29. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3564302/
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2019). Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER). Retrieved from: https://www.fda.gov/about-fda/fda-organization/center-biologics-evaluation-and-research-cber
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2018). What are "Biologics" Questions and Answers. Retrieved from: https://bit.ly/FDAWhatAreBiologics
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (n.d.). Biological Product Definitions. Retrieved from: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Biological-Product-Definitions.pdf
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (n.d.). CDER World: Biologics Review. Retrieved from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cderworld/index.cfm?action=newdrugs:main&unit=3&lesson=1&topic=1
- USP Compounding Expert Committee, (nd). General Chapter <797> Pharmaceutical Compounding – Sterile Preparations. Retrieved from: https://www.usp.org/compounding/general-chapter-797 [Accessed 11 November 2020].
- USP Compounding Expert Committee, (nd). General Chapter <800> Hazardous Drugs – Handling on Healthcare Settings. [ONLINE] available at: http://www.usp.org/sites/default/files/usp/document/our-work/healthcare-quality-safety/general-chapter-800.pdf. [Accessed 11 November 2020].
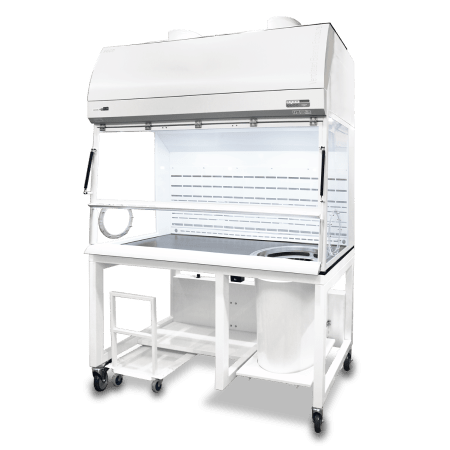
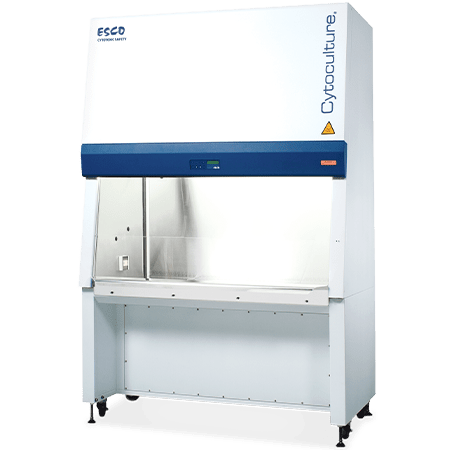
Recommended Products



.webp)










