
Discovery to Delivery
› Solutions ›Terminally Sterilized Products
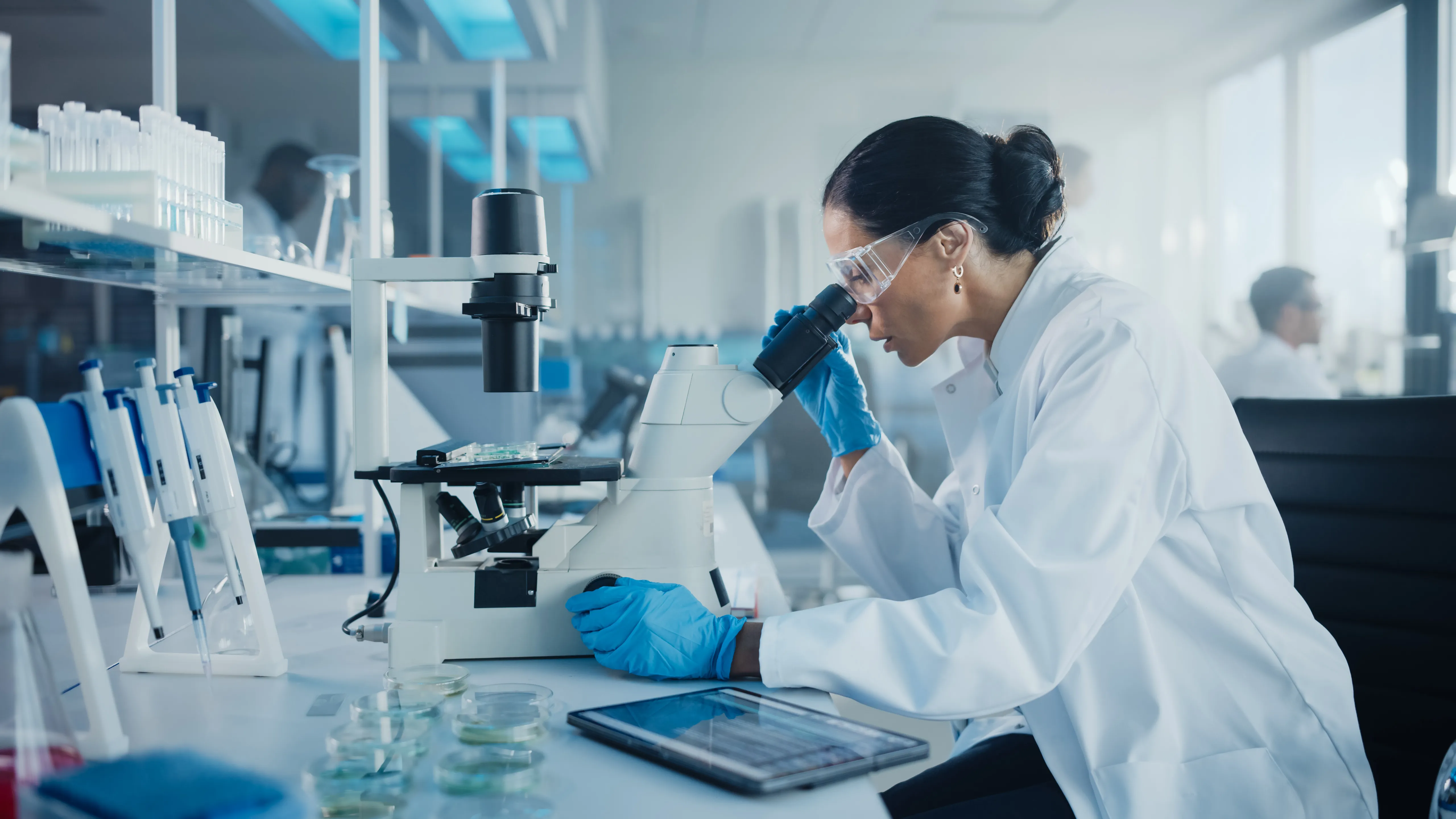
Injections are sterile, pyrogen limited, that is, bacterial endotoxin units limit, preparations intended to be administered parenterally. The term parenteral refers to the injectable routes of administration. It derives from the Greek words para (outside) and enteron (intestine) and denotes routes of administration other than the oral route. Pyrogens, or bacterial endotoxins, are organic metabolic products shed from Gram-negative bacteria which can cause fever and hypotension in patients when they are in excessive amounts in intravenous (IV) injections.
Intravenous Route - IV drugs provide rapid action compared with other routes of administration, and because drug absorption is not a factor, optimum blood levels may be achieved with accuracy and immediacy not possible by other routes. In emergencies, IV administration of a drug may be lifesaving because of the placement of the drug directly into the circulation and the prompt action that ensues.
Intramuscular Route - IM injections of drugs provide effects that are less rapid but generally longer lasting than those obtained from IV administration. Aqueous or oleaginous solutions or suspensions of drug substances may be administered intramuscularly. Depending on the type of preparation, absorption rates vary widely. Drugs in solution are more rapidly absorbed than those in suspension, and drugs in aqueous preparations are more rapidly absorbed than oleaginous preparations. The physical type of preparation is based on the properties of the drug itself and on the therapeutic goals
Subcutaneous Route - The SC route may be used for injection of small amounts of medication. Injection of a drug beneath the skin is usually made in the loose interstitial tissue of the outer upper arm, the anterior thigh, or the lower abdomen. The site of injection is usually rotated when injections are frequently given, as with daily insulin injections. Prior to injection, the skin at the injection site should be thoroughly cleansed.
Intradermal Route - A number of substances may be effectively injected into the corium, the more vascular layer of the skin just beneath the epidermis. These substances include various agents for diagnostic determinations, desensitization, or immunization.
Official Type of Injections
Characteristics of Large Volume Parenterals:
— They should not contain bacteriostatic agents or other pharmaceutical additives.They are employed for the following purposes:
These preparations refer to such pharmaceutical products that exert immunologic effects.
Storage
These solutions are intended to bathe or wash wounds surgical incisions or body tissues.
Examples are:
Dialysis is defined as a process whereby substances may be separated from one another in solution, by taking advantage of their differing diffusibility through membranes.
Types of Dialysis Solutions:
These solutions are allowed to flow into the peritoneal cavity to remove toxic substances normally excreted by the kidney. This dialysis solution contains:
• Dextrose, vitamins, minerals, electrolytes, amino acids or peptidesThe peritoneal dialysis solution containing hypertonic dialysis solution acts as a semi-permeable membrane and allows for the flow of undesired elements into the peritoneal dialysis fluid, which is removed by peritoneal tube to collection vessels.
These solutions are employed to remove toxins from the bloodstream.
In hemodialysis, the arterial blood is shunted (transferred or turned) through a polyethylene catheter, through a artificial dialyzing membrane, bathed in electrolyte solution.
Pellets are implanted under the skin (usually of the thigh, breast or abdomen), with a special injector device or by surgical incision.
Examples are:First Division: Product development
The ultimate objective of this department is to develop a sterile product with therapeutic effect in the patient.
Therefore the Product Development parenterals product considering the following factors:
I. Vehicle
Sources of Pyrogens
Ways of Destroying Pyrogens;
Pyrogens can be destroyed by heating at high temperatures, such as:II. Solutes
Factors to be considered in the choice of solutes:
III. Containers

Glass
Plastics
Rubber closures
Metal caps
IV. Formulation
Freeze dried or Lyophilized Parenteral Products
Characteristics of Freeze dried/lyophilized products
Parenteral emulsions
Effect of Route of Administrations
— The intended route of administration has a marked effect on the formulation of a parenterals product.V. Stability
This factor is considered by the Product development Division and should evaluate the effect of the components, particularly if the product is subjected to thermal sterilization.
Second Division: Product Area
Production Area includes all the steps in:
Environmental control
Maintenance of the aseptic area and sterile room is done by normal routine of cleaning of these areas at the end of the working day or during the night.
Methods of environmental control tests:
Air Sampling Technique
Collection of particulate matter from air through a clean, sterile membrane filterAdvantage: This sampler is portable and can be disinfected and hand carried whenever needed.
Exposure of nutrient agar plates to the settling of microorganisms from the air
If pathogenic microorganisms are particularly of interest, blood agar plates may be needed.
Note: A period of one hour may not collect one microorganism under conditions of use in a well controlled aseptic area.
Total Sterility Test
Use of instrumental scanners
Filtration of Parenteral Solutions
Solutions must be filtered for the following primary objectives:
Filter type & its Principal components
Filling of Parenteral Solutions:
Filling of Sterile Solids
Types of Ampoule sealing methods
Sealing of vials and bottles
Sterilization of Parenteral products
This is used to aid reduction of air borne contamination produced by mercury vapor lamps. This method has poor penetration capability. Its effectiveness depends on:
This radiation method makes use of high energy emitted from radioactive isotopes such as cobalt 60 (gamma rays) or by cathode or beta rays (mechanical acceleration of electrons to high velocity and energy).
Sign up to our newsletter and receive the latest news and updates about our products!
