How are ADCs Made?
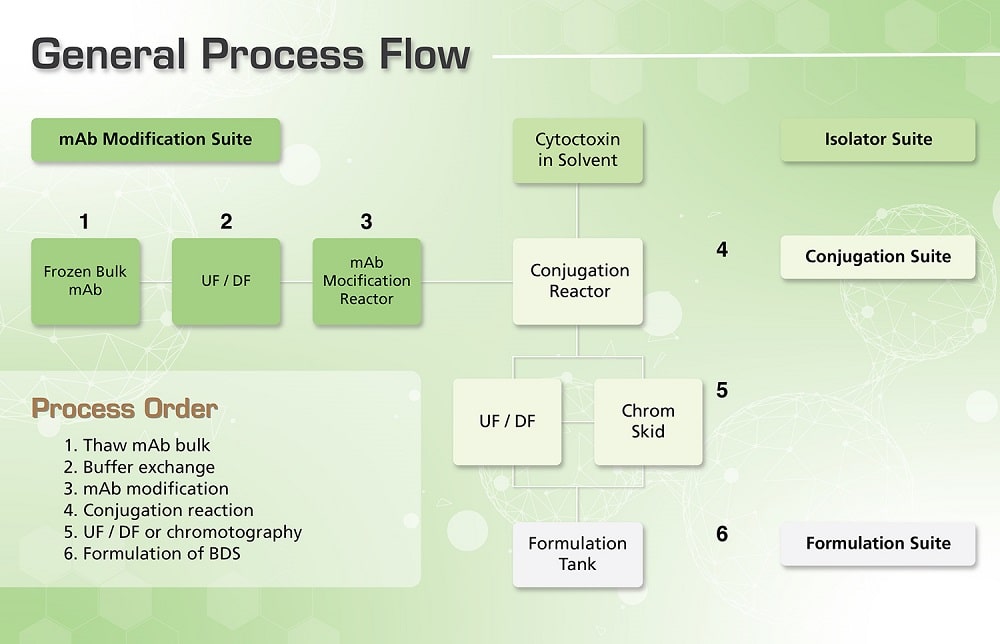
Figure 1. General workflow of ADC manufacture.
Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs) are the new class of highly potent biopharmaceutical drug with high specificity for cancer therapy. There are three components that make up an ADC: 1) a monoclonal antibody (mAb), 2) a linker, and 3) a biologically active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) with cytotoxic properties.
 Figure 2. Antibody drug conjugate parts.
Figure 2. Antibody drug conjugate parts.
These novel pharmaceuticals are target-specific since it can deliver highly potent cytotoxic drugs to the tumour site and not harm the healthy cells unlike conventional chemotherapy.
ADCs deliver deactivated cytotoxins to specific cancer cells. Once attached to the affected cell, the ADC internalizes into the cell and undergoes the process of receptor-mediated endocytosis wherein the cytotoxin is released, producing a cytotoxic activity. The final process leads to a rapid cancer cell death.
The design and synthesis of an effective ADC is challenging, requiring specialized equipment for the concept to be a reality.
In order to deliver quality antibody drug conjugates, these undergo a tedious process of manufacturing in very stringent conditions. Under strict containment, the process starts from dispensing and weighing of cytotoxic agents, up to packing-off the finished products.
Weighing and preparation of cytotoxins with organic solvents are done in an isolator, since it permits safe handling of cytotoxins in a negative pressure environment. The mixture is then transferred into a conjugation site by a hard-piped transfer line. The isolator must be designed with a Clean-In-Place (CIP) system that permits inactivation of the cytotoxin or other microbes which comes in contact with potent cytotoxins to remove the contamination.
In the conjugation site, the linking of the antibody and cytotoxin is performed inside a strict containment facility, in a sealed temperature and pH controlled stainless steel tank, with nitrogen overlay. Special equipment like double mechanical seals, overflow trays, and positive displacement pumps are also needed to strengthen personnel protection. After this process, the ADC contained in the buffer is transferred to the formulation site for bulk formulation.
All the wastes from the process are inactivated and incinerated on site, depending on the process requirements. After the cytotoxic agent concentration adjustment and excipient addition in the formulation site, the Bulk Drug Substance (BDS) is stored frozen at around -20 to -60 °C using a controlled freezer and aseptically dispensed into multiple PETG (polyethylene terephthalate glycol) bottles for bulk storage.
- Antibody-Drug Conjugate: Identity
- Generally more focus on mAb rather than drug-linker.
- Binding, charge based, peptide map, sequence based.
- The need for multiple assay depends on the properties/characteristics of the mAb/conjugate and if other conjugates are manufactured at the same facility.
- Charge based assays may not be possible/meaningful after conjugation lysine residues.
- Antibody-Drug Conjugate: Purity
- Largely the same methods as before conjugation.
- SDS-PAGE/CGE, SEC-HPLC, charge based.
- Charge based assays may not be possible/meaningful after conjugation to lysine residues.
- Need to control for aggregates and fragments.
- Need to understand what is stability indicating.
- Antibody-Drug Conjugate: Potency
- Mechanism of action is determined.
- Needs antigen binding for unconjugated mAb.
- Needs to demonstrate conjugation does not affect antigen binding.
- If conjugation process is well controlled, antigen binding assay may be eliminated provided cytotoxicity assay is robust.
Clinical ADC manufacturing must be executed in an aseptic biological manufacturing environment which operates under cGMP since the antibody modification and cytotoxin conjugation reaction are usually executed under process conditions which will support growth of environmental microbial contaminates. Batch failures resulting from human error or equipment failure are typically low for biological manufacturing.
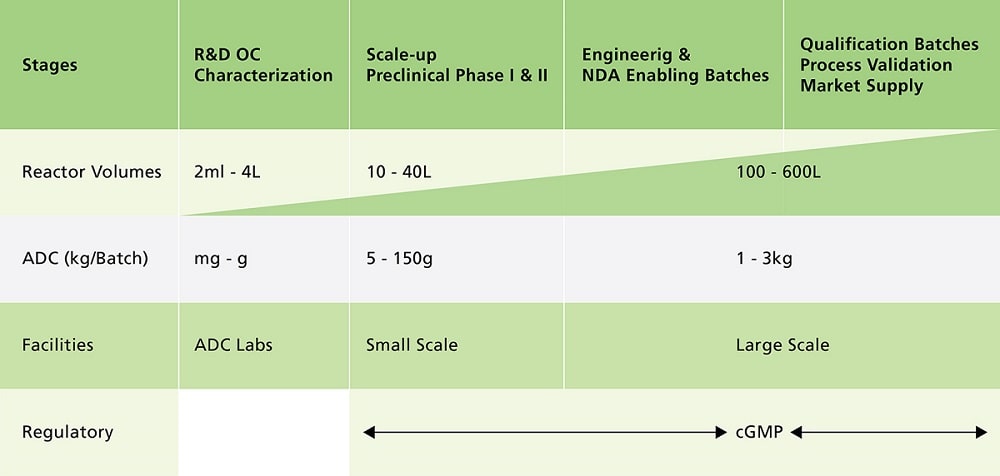 Figure 3. Stages of Manufacturing ADCs
Figure 3. Stages of Manufacturing ADCs
In the antibody modification suite the naked antibody raw material which is typically frozen at -20°C is thawed and the storage buffer is exchanged via tangential flow filtration. Buffer exchange is often required to alter the pH, salt concentration and remove excipients used to improve storage stability in the bulk antibody solution which may hinder or alter the performance of the conjugation reaction. These steps include the isolator used for weighing and preparation of the solution containing the cytotoxin (
Weighing and Dispensing Containment Isolator,
Containment Barrier Isolator, and
Aseptic Containment Isolator) and the conjugation suite, in which the cytotoxin is combined stoichiometrically with the antibody linker complex.
Bulk ultrafiltration or chromatography is then employed to remove process contaminants such as free cytotoxin and organic solvent.
References:
- ADC Review. (2016). What Are Antibody-Drug Conjugates or ADCs? Retrieved last 15 January 2018, from https://adcreview.com/adc-university/adcs-101/antibody-drug-conjugates-adcs/
Recommended Products





