
Discovery to Delivery
› Solutions ›Fine Chemicals and HPAPIs
Fine Chemicals and HPAPIs
Highly potent active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs) are pharmacologically active substances that exhibit biological activity at extremely low concentrations, such as daily therapeutic dose of <10 mg or an occupational exposure limit (OEL) of < 10 μg/m3 at an eight hour time-weighted average.
Each HPAPIs have specific OEL that must be considered by an institution to guarantee safe handling, as there is a selective process in choosing the most appropriate strategy for containment.
Recent Pharmaceutical Market
The continuous expansion of the biopharmaceutical market, particularly, the global demand in the field of medical oncology, calls for an increase in the development and conventional drug manufacturing of high potency active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs). Within the next 5 years, the value for cancer medication is estimated to reach 100 billion USD.
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), which use very toxic molecules specifically targeting cancer cells serve as one example for HPAPIs. These compounds represent an advancement in oncology treatment being highly potent cytotoxic drugs that do not harm the healthy cells unlike conventional chemotherapy.
The major problem with this is that human intervention is present at almost every stage of the manufacturing process, thus, increasing the risk for personnel exposure. This could lead to various adverse health effects to all personnel involved; that is why, ensuring the safety of the manufacturing personnel is of high importance. However, addressing this issue should not impede productivity.
In the manufacture of these highly potent compounds, specialized considerations are needed to be deliberated for the facility design, equipment, operation, and safety to achieve the best level of containment of the drug product.
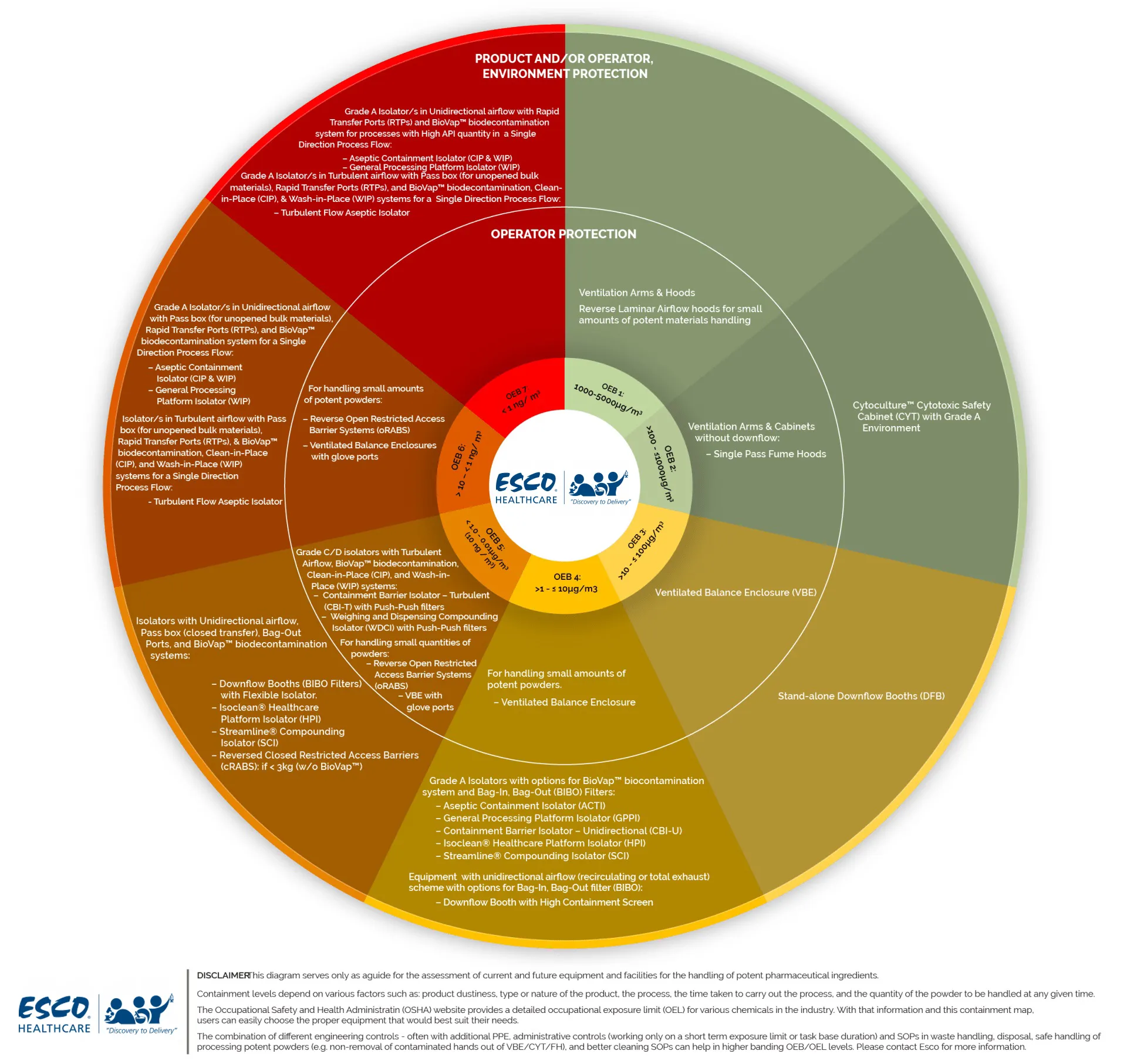

|
BAND |
OEB 1 |
OEB 2 |
OEB 3 |
OEB 4 |
OEB 5 |
OEB 6 |
OEB 7 |
|
OEL |
>1000 - 5000 µg/m3 |
>100 - ≤1000 µg/m3 |
>10 - ≤100 µg/m3 |
>1 - ≤10 µg/m3 |
<1.0 - 0.01 µg/m3 |
0.01 - 0.001 µg/m3 |
<0.001 µg/m3 - <1 ng/m3 |
|
Equipment
to Use |
Ventilation Containment |
Ventilation Containment or Flowhoods without downflow (single
pass Fume cabinets) |
Downflow Booths or VBEs, Flowhoods |
VBEs or DFBs with higher containment, Flowhoods with downflow
and inflow for small volume |
Isolators recommended however if handling less than 3kg and
short task duration, low dust cloud potential reverse oRABs possible |
Isolators |
Isolators |
|
Production OSD |
VBEs DFB with high containment screen |
WDCI DFB with flexible isolator |
WDCI |
WDCI |
|||
|
Production
common application |
Fume Hoods |
Downflow Booths |
Isolators |
||||
|
Production Injectable If Aseptic
needed (with HPV) |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator)
CBI-U (Containment Barrier Isolator Unidirectional)
|
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator)
CBI-U(Containment Barrier Isolator Unidirectional)
GPPI (General Processing Platform Isolator) with closed transfer |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator) With complete closed transfer (RTPs) |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator) With complete closed transfer (RTPs) |
|||
|
R&D Qc/ IPQC Sampling |
|
|
GPPI (General Processing Platform Isolator)
CBI-T (Containment Barrier Isolator Turbulent)
roRABs (Reverse open RABs) VBEs (if small quantity) |
||||
As the number of potent compounds in the pharmaceutical development continues to increase, the opportunities for HPAPI manufacturers will rise as well. At Esco Healthcare, the provision of the best product and service delivery is taken seriously. As we take on newer challenges, we are continuously soaring towards a greater progress. The issues regarding contamination for pharmaceutical, agricultural, medical, and production operations can be eliminated as we yield protection with containment.
References:
Recommended Products
Sign up to our newsletter and receive the latest news and updates about our products!
