Handling HPAPIs: Choosing the Best Containment Strategies

The determination of personnel and environmental potential exposure is usually required for the safe handling of high potency active pharmaceutical ingredients (HPAPIs). A selective process in selecting the most appropriate strategies is also a must for the assurance of containment.
HPAPIs are characterized by the occupational exposure limit (OEL) of at or lower than 10 micrograms per cubic meter of air (µg/m3). The lower the value, the more potent the compound; and the greater need for a higher level of containment is required. Their ability to target pathogens are more precise and more selective in comparison with the other conventional medicines in the market.
Antibody drug conjugates (ADCs), which use very toxic molecules specifically targeting cancer cells serve as one example for HPAPIs. These compounds represent an advancement in oncology treatment being highly potent cytotoxic drugs that do not harm the healthy cells unlike conventional chemotherapy.
In the manufacture of these highly potent compounds, specialized considerations are needed to be deliberated for the facility design, equipment, operation, and safety to achieve the best level of containment of the drug product.
The assurance of environmental and employee safety exposure would require specialized containment. The following factors show the facility design of a typical kilo-laboratory for HPAPI handling:
Room pressure controls designed for containment, including monitoring and verification, with the main HPAPI-handling area (negatively pressured area to the surrounding rooms)
Airlocks around the manufacturing and laboratory spaces must provide gowning and degowning area with proper pressure controls
Misting showers must be included in the degowning and exit areas to purge the personnel of any unwanted contaminants prior to the removal of personal protective equipment (PPE)
Only important trained employees must have access to the HPAPI-handling areas
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems must be designed for single-pass air with temperature, humidity, and particle controls
Safe-change filters inside isolators, ventilated enclosures, general HVAC exhaust system, etc., must be used in the filtration and capture of contaminants
Preventive maintenance and proper change-control procedures for the assurance of an effective operating equipment
Engineering controls are also a must in using HPAPIs, as they are the primary source of containment and isolation of potent compounds. There are five stages in the hierarchy of controls that define the best level of protection and it is as follows:
Product isolation: closed-system glassware and reactors, α/β valves
Containment equipment: isolators, ventilated laminar flow enclosures, rapid-transfer ports, local exhaust ventilation, closed-system cleaning via clean-in-place
Facility design: air pressurization, high number of air changes, single-pass air, restricted access, airlocks, safe-change filters, misting showers
PPE: chemical suits needed for solvents and reagents, coveralls and hoods, powered air-purifying respirator (PAPR), proper glove selection
Personnel: proper training, procedures and policies, education, health monitoring
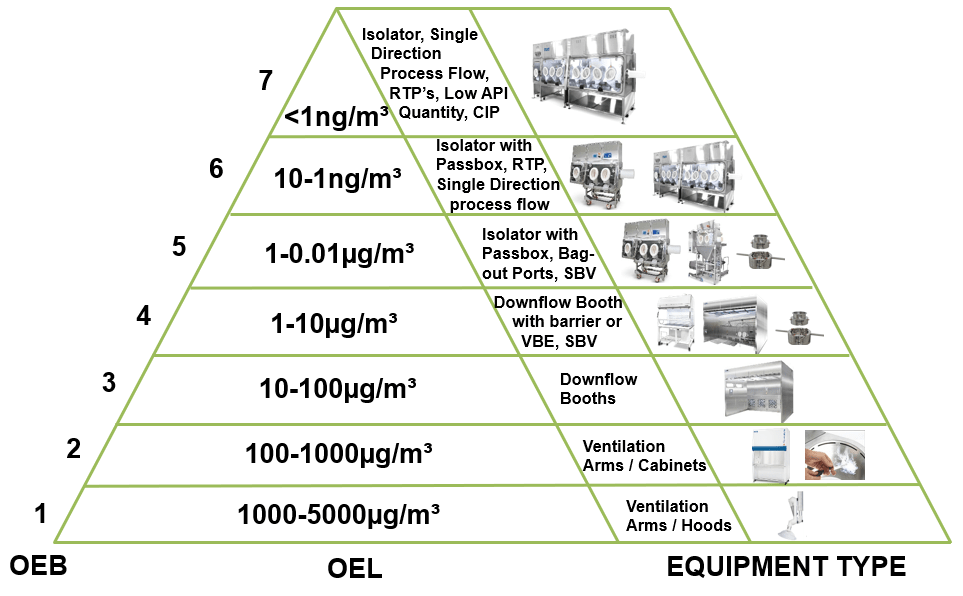
Figure 1. Operator exposure as defined by OEL/OEB with the appropriate Esco equipment for containment.
|
BAND |
OEB 1 |
OEB 2 |
OEB 3 |
OEB 4 |
OEB 5 |
OEB 6 |
OEB 7 |
|
OEL |
>1000 - 5000 µg/m3 |
>100 - ≤1000 µg/m3 |
>10 - ≤100 µg/m3 |
>1 - ≤10 µg/m3 |
<1.0 - 0.01 µg/m3 |
0.01 - 0.001 µg/m3 |
<0.001 µg/m3 - <1 ng/m3 |
|
Equipment
to Use |
Ventilation Containment |
Ventilation Containment or Flowhoods without downflow (single
pass Fume cabinets) |
Downflow Booths or VBEs, Flowhoods |
VBEs or DFBs with higher containment, Flowhoods with downflow
and inflow for small volume |
Isolators recommended however if handling less than 3kg and
short task duration, low dust cloud potential reverse oRABs possible |
Isolators |
Isolators |
|
Production OSD |
VBEs DFB with high containment screen |
WDCI DFB with flexible isolator |
WDCI |
WDCI |
|||
|
Production
common application |
Fume Hoods |
Downflow Booths |
Isolators |
||||
|
Production Injectable If Aseptic
needed (with HPV) |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator)
CBI-U (Containment Barrier Isolator Unidirectional)
|
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator)
CBI-U(Containment Barrier Isolator Unidirectional)
GPPI (General Processing Platform Isolator) with closed transfer |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator) With complete closed transfer (RTPs) |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator) With complete closed transfer (RTPs) |
|||
|
R&D Qc/ IPQC Sampling |
|
|
GPPI (General Processing Platform Isolator)
CBI-T (Containment Barrier Isolator Turbulent)
roRABs (Reverse open RABs) VBEs (if small quantity) |
||||
Table 1. OEB/OEL with further recommendations of Esco containment equipment.
As the number of potent compounds in the pharmaceutical development continues to increase, the opportunities for HPAPI manufacturers will rise as well. At Esco Pharma, the provision of the best product and service delivery is taken seriously. As we take on newer challenges, we are continuously soaring towards a greater progress. The issues regarding contamination for pharmaceutical, agricultural, medical, and production operations can be eliminated as we yield protection with containment.
References:
-
1. Cleanroomtechnology.com (2018) Containment strategy for highly potent API manufacturing. Accessed last 24 January 2019 from https://www.cleanroomtechnology.com/news/article_page/Containment_strategy_for_highly_potent_API_manufacturing/149845
-
2. Lazarro, O. (2016) Choosing Containment Strategies For Highly Potent APIs. Accessed last 24 January 2019 from http://www.pharmtech.com/choosing-containment-strategies-highly-potent-apis
-
3. Pharmtech.com (2008) High-Potency APIs: Containment and Handling Issues. Accessed last 24 January 2019 from http://www.pharmtech.com/high-potency-apis-containment-and-handling-issues?id=&sk=&date=&%0A%09%09%09&pageID=3
-
4. Van Arnum, P. (2009) Examining High-Potency API Manufacturing. Accessed last 24 January 2019 from http://www.pharmtech.com/examining-high-potency-api-manufacturing
Contact Us
Esco Pharma Pte. Ltd.
21 Changi South Street 1 Singapore 486777
Tel: +65 65420833
Fax: +65 65426920
Email: [email protected]
Esco Technologies, Inc.
Esco Pharma Factory
2512 Metropolitan Dr. Suite 120-B
Feasterville-Trevose, PA 19053-6738
Tel: +1 215-322-2155
Email: [email protected]
Esco GB Ltd.
Unit 2 R-Evolution @ Gateway 36
Kestrel Way, Barnsley, S70 5SZ
Tel: +44 (0) 1226 360799
Email: [email protected]
About our BRANDS
Esco Pharma provides specialist services, equipment packages, and process solutions from our core platform products leading to improved operator protection, reduction of cross contamination, and more efficient processing, thereby directly and indirectly advancing occupational health and human healthcare.
About Esco Pharma
Esco Pharma's largest global network of localized application specialists and service offices provides faster response and local service translating into more competitive costs on maintenance, and shorter project life cycles..
Esco provides standardized platforms with inbuilt configurations without constraints on operational parameters. This enables pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmeceuticals to comply with international standards for occupational health and safety.





