
Discovery to Delivery
› Solutions ›OEL / OEB
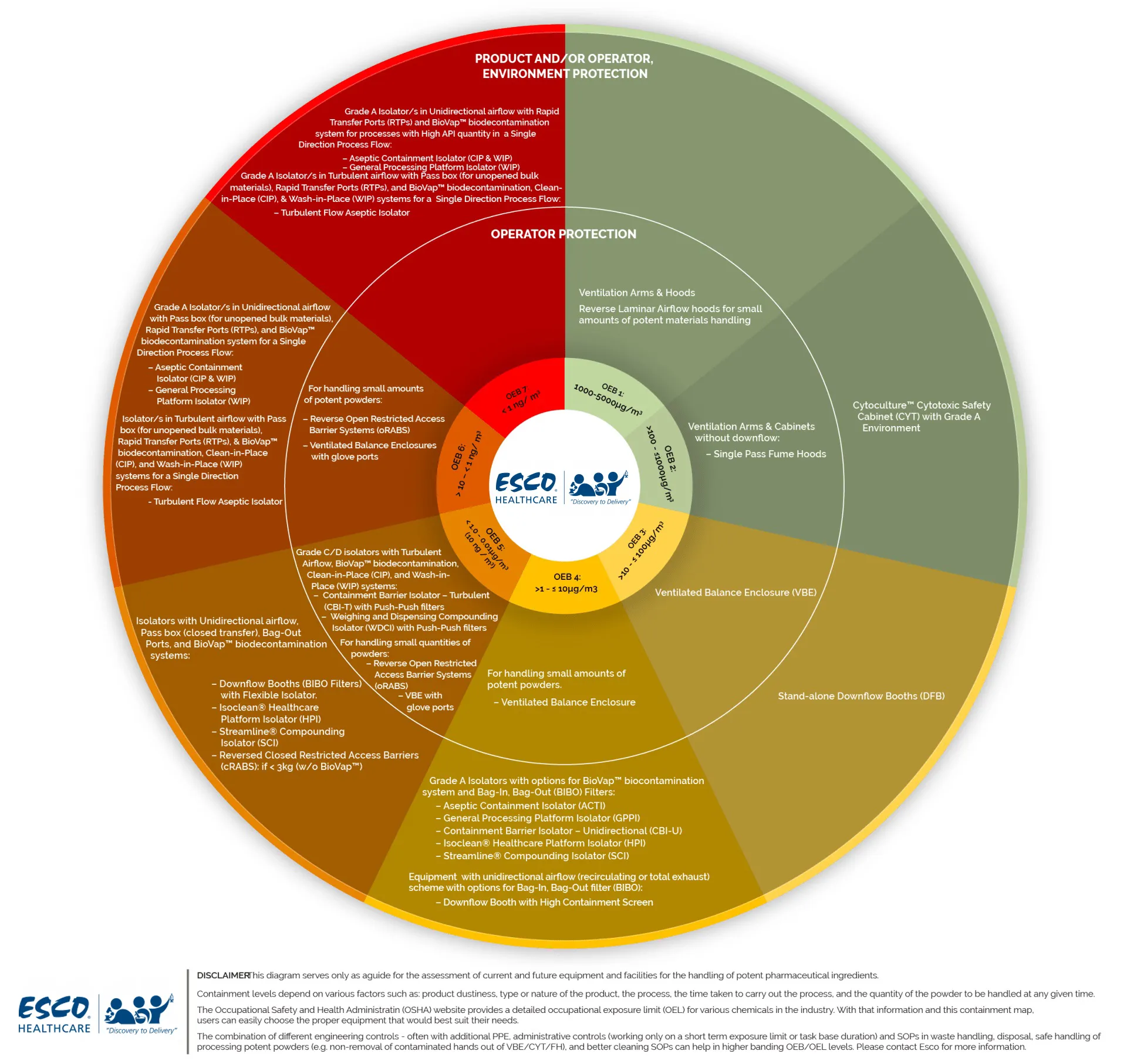
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API) have the prospect to bring about severe to serious health effects in personnel at very low airborne concentrations. The use of containment systems or equipment, as an integral part of an efficient method to potent compound safety, is recommended to control personnel exposure.
APIs can be classified into control bands based on their potency. Generally, APIs are categorized by occupational exposure limit (OEL) as a classification measure.
Terms:
OEB – Occupational Exposure Band ia a mechanism used to precisely assign chemicals into “categories” or “bands” based on their adverse health outcomes and potency considerations. It also aligns chemicals in groupings based on OEL in order to establish safe handling guidelines.
*Almost every facility has their own version
Hazard Banding (OEB) Criteria:
These include qualitative, semi‐quantitative, and quantitative data for each toxicological endpoint.
OEL – Occupational Exposure Limit is the airborne concentration of a compound to which nearly all workers can be repeatedly be exposed to for 8 hours a day, 40 hours a week, without adverse effects.
These are values set to prevent occupational diseases, notably in personnel exposed to harmful chemicals in the workplace. OELs are often expressed in mg/m3 especially for metals, salts and other compounds that do not form vapours at room temperature and pressure. However, some OELs may be expressed in units such as fibres/cc while a few are expressed in parts per million (ppm) if the substance exists as a gas or vapour at normal room temperature and pressure.

| OEB | OEL Range µg/m3 | Toxicological/Pharmacological Properties and potency | Esco Containment Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1000-5000 | Not harmful, not irritating, low pharmacological activity | Esco Standard Pharmacon Downflow Booth with no additional engineering controls. |
| 2 | 100-1000 | Harmful, possible irritant, mid pharmacological activity | Esco Standard Pharmacon Downflow Booth with no additional engineering controls. May require additional engineering controls if the process is extremely dusty (e.g. milling). |
| 3 | 50-100 | Moderate toxicity high pharmacological activity | Esco Standard Pharmacon Downflow Booth may require additional engineering controls dependent on quantity handled and the process operation. |
| 4 | 1-50 | Toxic, corrosive, genotoxic, cytotoxic | Esco Custom Pharmacon Downflow Booth with additional engineering control: 1.) Drum lifters 2.) Physical Barriers 3.) High containment enclosures with glove ports 4) Architectural features (e.g. airlocks/controlled access) to lower cross contamination risk Note application would have to be assessed for suitability. Dependent on process/product the use of Isolator (glovebox) technology may be recommended. |
| 5 | <1 | Extremely toxic, may be corrosive, sensitizing | Esco strongly recommends use of Isolator (glovebox) technology at this OEL level. Can be incorporated as part of custom Pharmacon Downflow Booth. |
Additional recommendations:
|
BAND |
OEB 1 |
OEB 2 |
OEB 3 |
OEB 4 |
OEB 5 |
OEB 6 |
OEB 7 |
|
OEL |
>1000 – 5000 µg/m3 |
>100 – ≤1000 µg/m3 |
>10 - ≤100 µg/m3 |
>1 – ≤10 µg/m3 |
<1.0 µg/m3 – 0.01 µg/m3 10 ng/m3 |
0.01 µg/m3 to 0.001 µg/m3 >10 ng/m3< 1 ng/m3 |
<0.001µg/m3 - <1 ng/m3 |
|
Equipment to Use |
Ventilation Containment |
Ventilation Containment or Flowhoods without downflow (single pass Fume cabinets) |
Downflow Booths or VBEs, Flowhoods |
VBEs or DFBs with higher containment, Flowhoods with downflow and inflow for small volume |
Isolators recommended however if handling less than 3kg and short task duration, low dust cloud potential reverse oRABs possible. |
Isolators |
Isolators |
|
Production OSD |
|
|
|
VBEs DFB with high containment screen |
WDCI DFB with flexible isolator |
WDCI |
WDCI |
|
Production common application |
|
Fume Hoods - protect the user from inhaling toxic gases (fume hoods, biosafety cabinets, glove boxes) - protect the product or experiment (biosafety cabinets, glove boxes) - protect the environment (recirculating fume hoods, certain biosafety cabinets, and any other type when fitted with appropriate filters in the exhaust airstream) - Secondary functions of these devices may include explosion protection, spill containment, and other functions necessary to the work being done within the device. |
Downflow Booths - Open handling of highly hazardous powders. Most commonly used in the Pharmaceutical, Cosmetic, Fine Chemical and Nanotechnology Industries. - Operator protection during potent or non-potent manual powder/compound handling operations such as: weighing and sampling of raw materials, manufacture of tablets and capsules, packaging, charging and dispensing. |
Isolators - designed to provide worker protection from exposure to undesirable levels of airborne drug throughout the compounding and material transfer processes and to provide an aseptic environment for compounding sterile preparations - Designed for compounding pharmaceutical ingredients or preparations. It is designed to maintain an aseptic compounding environment within the isolator throughout the compounding and material transfer processes. - For handling New Chemical Entities, weighing, dispensing and containing potent compounds during sub-division and sampling processes. |
Isolators - designed to provide worker protection from exposure to undesirable levels of airborne drug throughout the compounding and material transfer processes and to provide an aseptic environment for compounding sterile preparations - Designed for compounding pharmaceutical ingredients or preparations. It is designed to maintain an aseptic compounding environment within the isolator throughout the compounding and material transfer processes. - For handling New Chemical Entities, weighing, dispensing and containing potent compounds during sub-division and sampling processes. |
Isolators - designed to provide worker protection from exposure to undesirable levels of airborne drug throughout the compounding and material transfer processes and to provide an aseptic environment for compounding sterile preparations - Designed for compounding pharmaceutical ingredients or preparations. It is designed to maintain an aseptic compounding environment within the isolator throughout the compounding and material transfer processes. - For handling New Chemical Entities, weighing, dispensing and containing potent compounds during sub-division and sampling processes. |
Isolators - designed to provide worker protection from exposure to undesirable levels of airborne drug throughout the compounding and material transfer processes and to provide an aseptic environment for compounding sterile preparations - Designed for compounding pharmaceutical ingredients or preparations. It is designed to maintain an aseptic compounding environment within the isolator throughout the compounding and material transfer processes. - For handling New Chemical Entities, weighing, dispensing and containing potent compounds during sub-division and sampling processes. |
|
Production Injectable If Aseptic needed (with HPV) |
|
|
|
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator) |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator) CBI-U(Containment Barrier Isolator Unidirectional) GPPI (General Processing Platform Isolator) with closed transfer |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator) With complete closed transfer (RTPs)
|
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator) With complete closed transfer (RTPs)
|
|
R&D Qc/ IPQC Sampling |
|
|
GPPI (General Processing Platform Isolator) roRABs (Reverse open RABs) VBEs (if small quantity) |
|
BAND |
OEB 1 |
OEB 2 |
OEB 3 |
OEB 4 |
OEB 5 |
OEB 6 |
OEB 7 |
|
OEL |
>1000 - 5000 µg/m3 |
>100 - ≤1000 µg/m3 |
>10 - ≤100 µg/m3 |
>1 - ≤10 µg/m3 |
<1.0 - 0.01 µg/m3 |
0.01 - 0.001 µg/m3 |
<0.001 µg/m3 - <1 ng/m3 |
|
Equipment
to Use |
Ventilation Containment |
Ventilation Containment or Flowhoods without downflow (single
pass Fume cabinets) |
Downflow Booths or VBEs, Flowhoods |
VBEs or DFBs with higher containment, Flowhoods with downflow
and inflow for small volume |
Isolators recommended however if handling less than 3kg and
short task duration, low dust cloud potential reverse oRABs possible |
Isolators |
Isolators |
|
Production OSD |
VBEs DFB with high containment screen |
WDCI DFB with flexible isolator |
WDCI |
WDCI |
|||
|
Production
common application |
Fume Hoods |
Downflow Booths |
Isolators |
||||
|
Production Injectable If Aseptic
needed (with HPV) |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator)
CBI-U (Containment Barrier Isolator Unidirectional)
|
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator)
CBI-U(Containment Barrier Isolator Unidirectional)
GPPI (General Processing Platform Isolator) with closed transfer |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator) With complete closed transfer (RTPs) |
ACTI (Aseptic Containment Isolator) With complete closed transfer (RTPs) |
|||
|
R&D Qc/ IPQC Sampling |
|
|
GPPI (General Processing Platform Isolator)
CBI-T (Containment Barrier Isolator Turbulent)
roRABs (Reverse open RABs) VBEs (if small quantity) |
||||
It should be noted that these bands are rules of thumb for guidance only.
Each application must be assessed based on the following criteria:
References:
Affygility Solutions. (2017). Potent Compound Corner: What is an occupational exposure limit and why are they important?. Retrieved from: https://affygility.com/potent-compound-corner/2017/10/11/what-is-an-occupational-exposure-limit-and-why-are-they-important.html
Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. (2016). Converting Occupational Exposure Limits from mg/m3 to ppm. Retrieved from: https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/chemicals/convert.html?print
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019). NIOSH Occupational Exposure Banding e-Tool. Retrieved from: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Niosh-oeb/?s_cid=3ni7d2eNews-OEB-Tool-July2019
Ripple, S. (n.d.). Health Hazard Banding: Occupational Exposure Banding [PowerPoint Presentation]. Tera. Retrieved from: https://www.tera.org/OARS/Presentations/Hazard%20Banding%20Workshop%20IHRT.pdf
Recommended Products
Sign up to our newsletter and receive the latest news and updates about our products!
